Comments
Comments are used to improve code readability by providing explanations or notes within the source code. They help developers understand the logic or intent behind specific code blocks.
Example:
// This class represents the Student Object
class Student {
// This field represents the property of the Student Object
String name;
// This represents the behaviour of the Student Object
void writing() {
System.out.println("Student is writing");
}
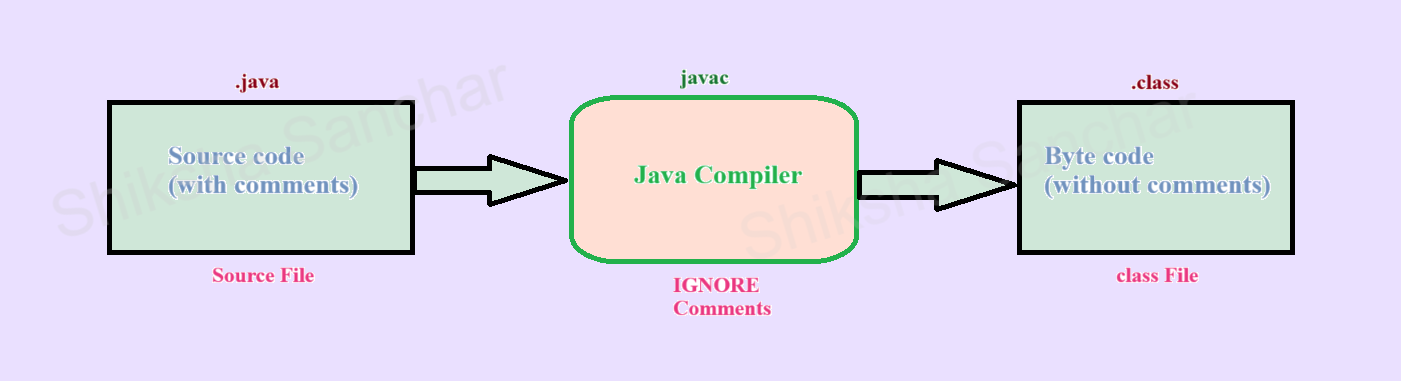
}Note: However, the information specified as comments will be ignored by the compiler at the time of compilation. It means, the compiled code will not have any information specified as comments. Hence, comments do not affect the output or performance of the program.
Diagram for understanding comments:
Types of Comments in Java:
1. Single-line comment :
Used for short, one-line explanations.
// This is a single line comment2. Multi-line comment :
Used for longer explanations or blocks.
/* This
is a
Multi-line
comment */3. Documentation Comments (Javadoc) :
Used for generating API documentation using the javadoc tool.
/**
* This class defines a Student entity.
* @author ShikshaSanchar
* @version 1.8
*/
class Student {
String name;
}Summary:
- Comments are used to explain code, making it more readable and maintainable.
- They are ignored by the compiler and do not affect program execution.
- Java supports three types of comments:
- Single-line (
//) - Multi-line (
/* */) - Documentation (Javadoc) (
/** */) – used to generate official documentation.
- Single-line (
- Using meaningful comments improves collaboration, debugging, and future code updates.