Variables
What is a Variable?
A variable is a name given to a memory location in RAM. It stores data that can change during program execution.
The term "variable" comes from:
“vary” + “able” → meaning "able to change".
A variable is also known as an alias, meaning a nickname for a memory location. When we refer to a variable, we're indirectly accessing the memory where the value is stored.
Key Points :
- A variable must be declared before use.
- It is used to store data temporarily in memory.
- Its value can be updated during program execution.
Types of Variable Operations
| Operation | Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration | int a; |
Reserves memory for a |
| Assignment | a = 10; |
Stores value 10 into a |
| Initialization | int a = 10; |
Declares and assigns in one step |
Java Program:
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 100; // initialization -> declaring & assigning value
System.out.println(a); // using variable
a = 150; // assignment
System.out.println(a); // using variable
}
}Output:
100
150
Explanation:
- Step 1:
int a = 100;
→ A memory space is created in RAM for variable a and value 100 is stored. - Step 2:
System.out.println(a);
→ Java reads value of a from RAM and prints 100. - Step 3:
a = 150;
→ The value in memory is updated from 100 to 150. - Step 4:
System.out.println(a);
→ Now prints the updated value: 150.
Memory Diagram for the above example:
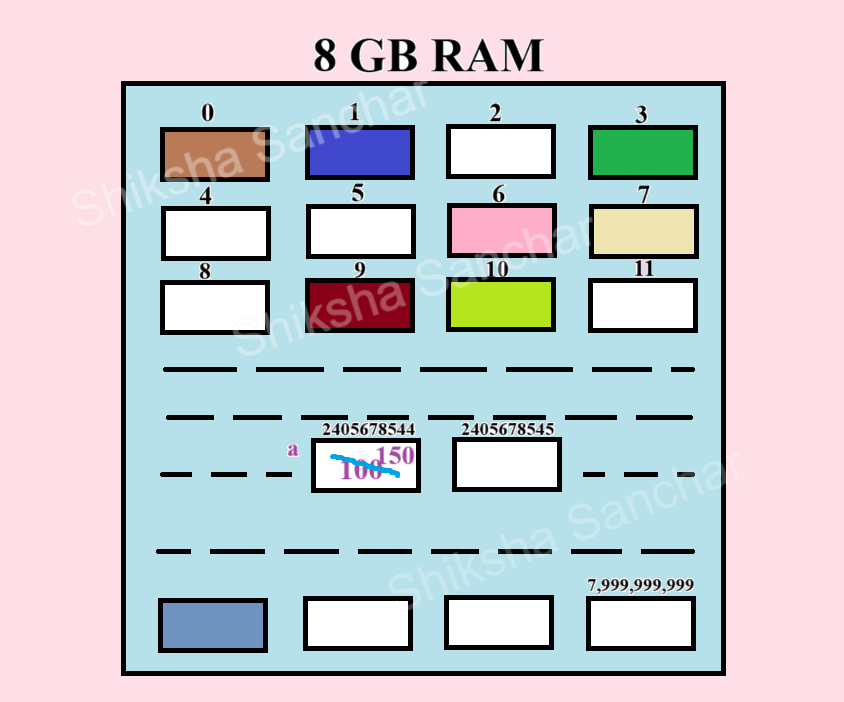
Multiple Variable Declarations and Initializations
Separate Declaration
int a;
int b;
int c;Combined Declaration
int a, b, c;Separate Initialization
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 30;Combined Initialization
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 30;Same Value to All
int c, b, a;
a = b = c = 10; // Assigns 10 to allNote (Important Concept)
int a, b, c = 10;- Here, only c is initialized with 10.
- a and b are just declared, not assigned any value.
- This is a common beginner mistake — assuming all are assigned 10.
Summary:
- A variable is a symbolic name for a memory location that stores data.
- It must be declared before use, and can optionally be assigned or initialized.
- Java supports multiple ways of declaring and initializing variables.
- A variable is also an alias to the memory location.
- Be careful with partial initialization in lines like
int a, b, c = 10;— only c gets the value.