Data Types in Java
Definition
A data type in Java is a classification that specifies the type of data a variable can hold, the amount of memory to be allocated, and the set of operations that can be performed on it.
Computers can only understand binary digits (0s and 1s). But in real life, we deal with different kinds of information like names, ages, dates, documents, images, and videos. To make this data usable for a computer, Java provides data types.
Data types act as a bridge between real-world data and computer memory. They not only decide what kind of data can be stored, but also how much memory will be allocated in RAM and how the CPU will process it.
Roles of Data Types
- Conversion – Convert real-world data into binary form so it can be stored and processed.
- Memory Allocation – Indicate how much memory should be reserved in the RAM.
- Type Specification – Define the kind of value (number, text, boolean, file, etc.) a variable can hold.
- Operation Control – Specify what operations are allowed (e.g., numbers can be added, but strings are concatenated).
Example (Real World → Java → Binary)
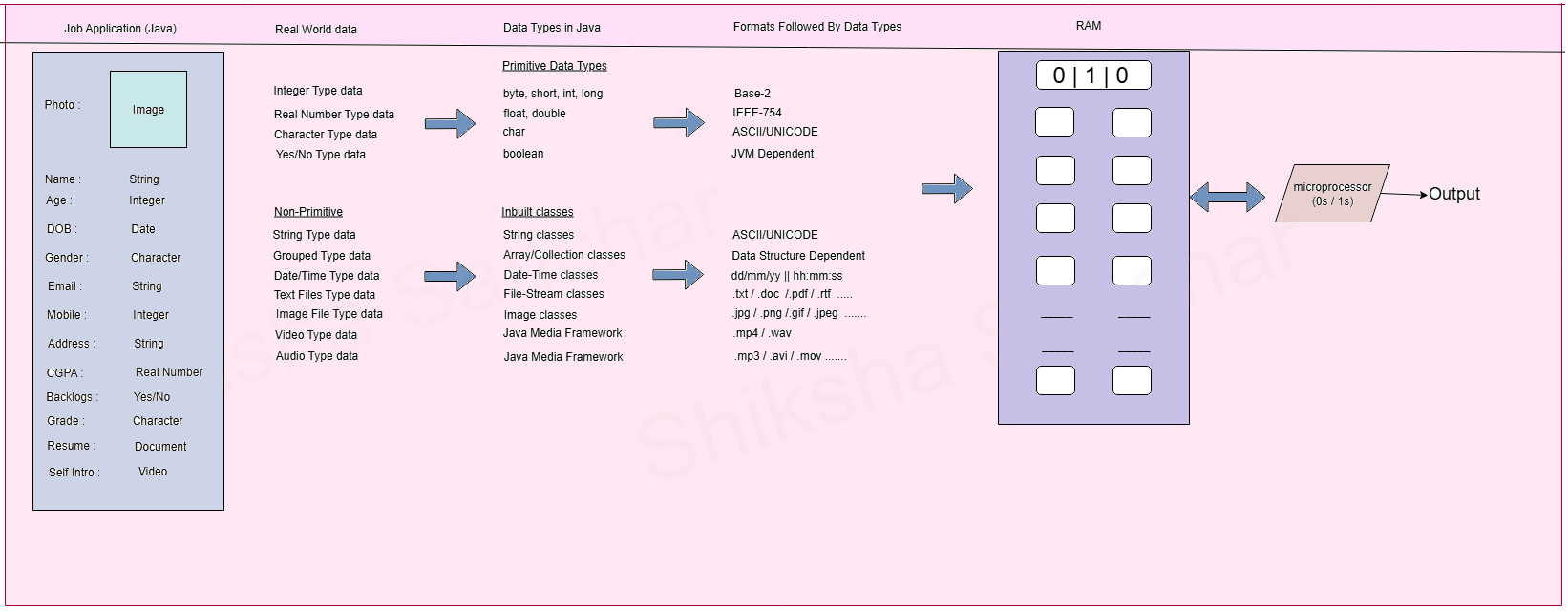
- Name → stored as String.
- Age → stored as int.
- Date of Birth (DOB) → stored as Date.
- Resume → stored as Document (File type).
- Self Intro Video → stored as Video type.
Java internally divides these into:
- Primitive Data Types – byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, boolean.
- Non-Primitive Data Types – String, Arrays, Classes, Interfaces, Enums, File types, Multimedia frameworks.
Behind the Scenes
When a variable is declared in Java:
- Text is stored using ASCII/Unicode.
- Numbers are stored using IEEE-754 standard (for floating-point).
- Objects and files are stored in JVM-dependent formats.
All this data is stored in RAM as binary (0s and 1s), and the microprocessor processes it to produce the final output.
Summary:
A data type in Java defines the kind of data a variable can store, the memory it needs, and the operations allowed on it. It converts real-world data into binary form so it can be stored in RAM and processed by the CPU.
Java provides Primitive (int, char, boolean, etc.) and Non-Primitive (String, Arrays, Classes, etc.) data types.